Kattampally Dam things to do, attractions, restaurants, events info and trip planning
Basic Info
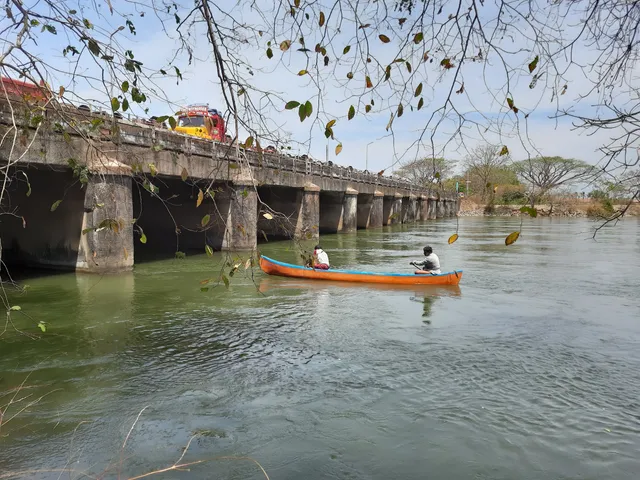
Kattampally Dam
W9MG+XFC, Chirakkal - Mayyil - Kololam Rd, Kattampally - Kottali Road, Kerala 670011, India
4.1(9)
Open until 12:00 AM
Save
spot
spot
Ratings & Description
Info
Outdoor
Scenic
Relaxation
Family friendly
attractions: Kattampally Kayaking, restaurants: , local businesses:
 Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.
Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.Open hoursSee all hours
FriOpen 24 hoursOpen
Plan your stay

Pet-friendly Hotels in Kerala
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Affordable Hotels in Kerala
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

The Coolest Hotels You Haven't Heard Of (Yet)
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Trending Stays Worth the Hype in Kerala
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.
Reviews
Live events
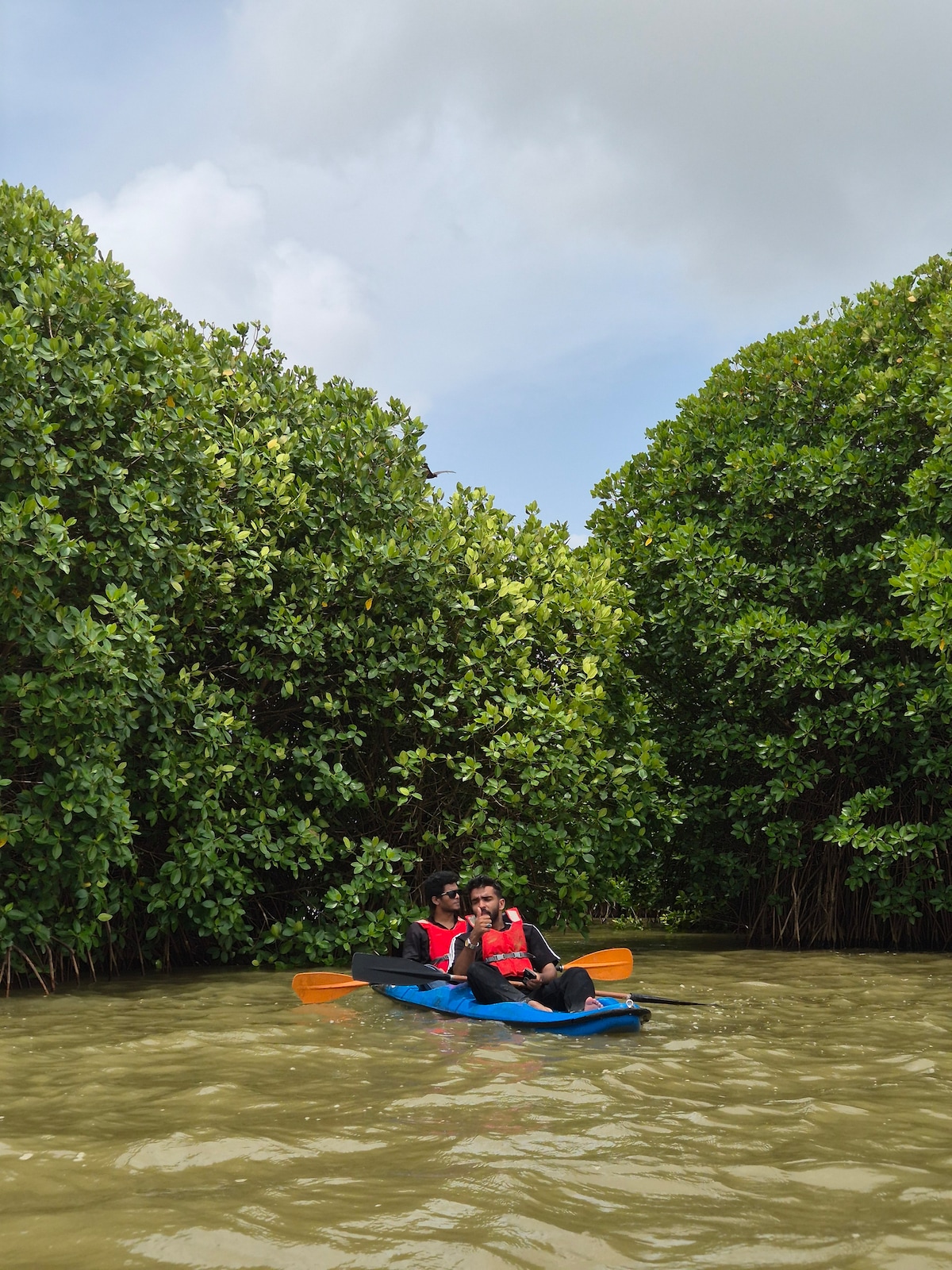

Kayak the Calm Waters of Pulloopi
Fri, Feb 20 • 4:30 PM
Puzhathi, Kerala, 670005, India
View details
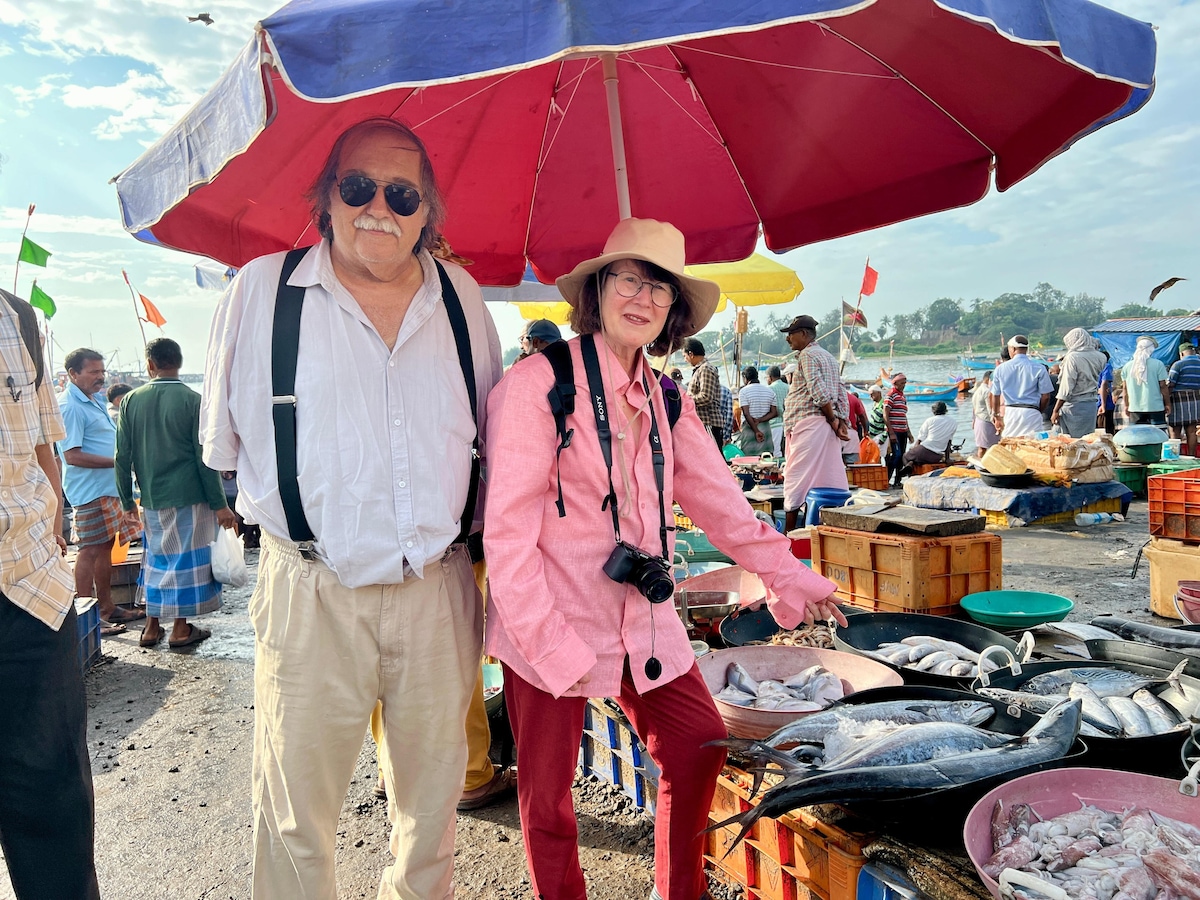

Devour Malabari cuisine in Kannur
Sat, Feb 21 • 9:30 AM
kanhirode Kanhirode, Kerala, 670592, India
View details
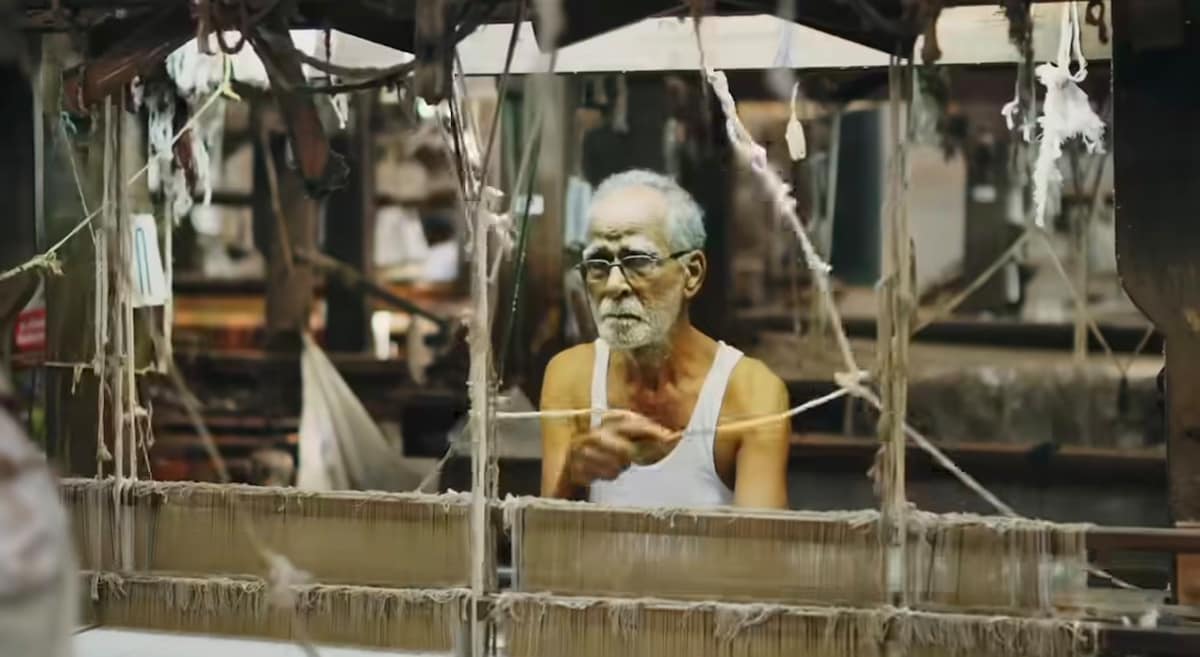

Weavers of Kannur with a fifth generation weaver
Sat, Feb 21 • 10:30 AM
Kannur, Kerala, 670002, India
View details
Nearby attractions of Kattampally Dam
Kattampally Kayaking
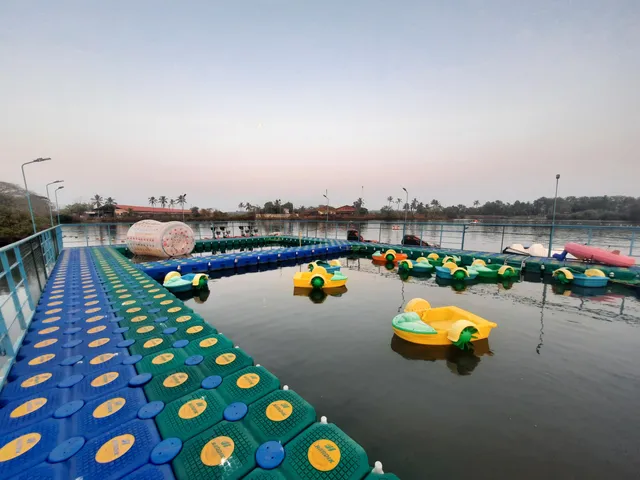

Kattampally Kayaking
4.3
(141)
Open until 7:00 PM
Click for details