Selama beberapa dekade setelah serangkaian penemuan lukisan gua di gua-gua batu kapur di Maros, Sulawesi Selatan, para ilmuwan berpendapat bahwa kemungkinan lukisan itu telah dibuat lebih dari 10.000 tahun yang lalu. Mereka beralasan bahwa Iklim lembab wilayah Sulawesi akan menghancurkan sesuatu yang lebih tua.
Namun menurut temuan penelitian baru yang dilaporkan pada jurnal Nature, lukisan-lukisan gua Sulawesi ternyata jauh lebih tua dari yang diperkirakan sebelumnya, dan mungkin sebenarnya dianggap setua seni gua paling awal yang ditemukan di Eropa.
Dipimpin oleh Maxime Aubert dan Adam Brumm dari Griffith University di Queensland, Australia, sebuah tim peneliti Indonesia dan Australia menetapkan usia lukisan gua di Sulawesi, dengan memeriksa lapisan kalsium karbonat bergelombang yang terbentuk di atasnya menggunakan teknik yang dikenal sebagai kencan uranium-thorium.
Dengan mengukur tingkat peluruhan uranium saat berubah menjadi thorium, para ilmuwan dapat memperkirakan usia lapisan mineral hingga tingkat akurasi yang tinggi. Karena kerak ini agaknya lebih muda dari karya seni yang diliputinya, proses penanggalan memberi mereka usia minimum untuk lukisan di bawahnya.
Setelah memeriksa 12 gambar tangan manusia dan dua gambar hewan yang ditemukan di dinding tujuh gua yang berbeda, para peneliti menemukan bahwa satu gambar tangan setidaknya berusia 39.900 tahun.
Meskipun praktik meniup atau menyemprotkan pigmen di sekitar tangan yang ditekan ke permukaan batu akan menjadi hal yang umum di antara para seniman gua selama berabad-abad (dan berlanjut di antara anak-anak sekolah saat ini), citra Sulawesi tampaknya menjadi contoh paling awal dari jenisnya, sekitar 2.000 tahun lebih tua dari usia minimum lukisan cap tangan tertua di Eropa.
Selain itu, para ilmuwan menemukan bahwa salah satu lukisan yang menggambarkan hewan yang dikenal sebagai babirusa, sudah ada sejak 35.300 tahun yang lalu. Meskipun lukisan cap tangan tampak mirip dengan yang ditemukan di Eropa, namun gambar binatang pada gua di Sulawesi Selatan memiliki gaya yang sangat berbeda.
Menurut Alistair Pike, seorang arkeolog di University of Southampton, Inggris, menyatakan bahwa gambar yang ditemukan di Indonesia terlihat hampir seperti sapuan kuas, sedangkan gambar pada gua di Eropa terlihat dioleskan menggunakan tangan.
Dalam beberapa tahun terakhir, para arkeolog telah menggunakan teknik penanggalan serupa untuk memperkirakan usia lukisan gua tertua yang telah ditemukan di Eropa, sebuah cakram merah yang dilukis di dinding sebuah gua Spanyol bernama El Castillo yang berusia setidaknya 40.800 tahun. Penggambaran paling awal tentang hewan yang ditemukan di Eropa adalah badak yang dilukis di dinding Gua Chauvet Prancis, yang telah berusia antara 35.300 hingga 38.827 tahun yang lalu.
Penemuan seni gua di Sulawesi tampaknya telah mematahkan teori sebelumnya yang menyatakan bahwa lukisan dinding tertua hanya ditemukan di Eropa Barat sekitar 40.000 tahun yang lalu. Seperti yang dikatakan Aubert: “Ada beberapa gagasan bahwa orang Eropa awal lebih sadar akan diri mereka sendiri dan lingkungan mereka. Sekarang kita dapat mengatakan itu tidak benar.”
Sebaliknya, tradisi kreatif lukisan dinding gua mungkin muncul secara terpisah pada waktu yang sama di berbagai sisi dunia. Penelitian baru tampaknya mendukung teori ini, menurut pemimpin penelitian Brumm: “Lukisan gua dan bentuk-bentuk ekspresi artistik yang terkait kemungkinan besar adalah bagian dari tradisi budaya manusia modern pertama yang menyebar ke Afrika dan ke Asia dan Australia, lama sebelum mereka mencapai Eropa."
Beberapa ilmuwan lebih suka teori bahwa seni gua dimulai di Afrika, meskipun situs arkeologi di Afrika cenderung terletak di gua dangkal di mana kondisinya tidak ideal untuk melestarikan karya seni seperti itu, bukti penggunaan pigmen, ukiran dan perhiasan pribadi seperti manik-manik dan perhiasan lainnya menunjukkan kepekaan artistik manusia jauh sebelum mereka bermigrasi ke...
Read more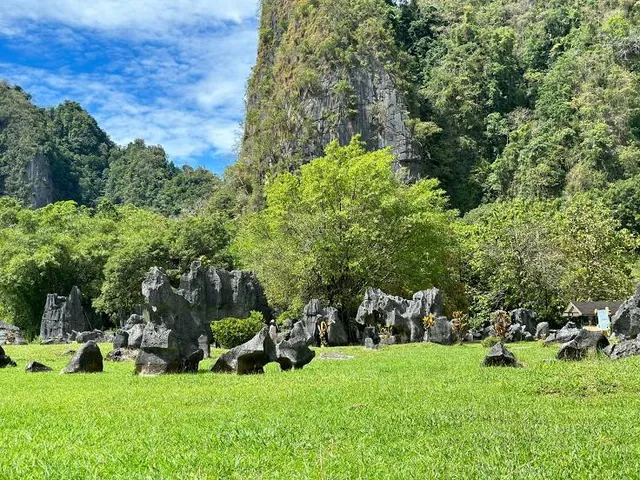
 Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.
Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.