Knidos Ancient City things to do, attractions, restaurants, events info and trip planning
Basic Info
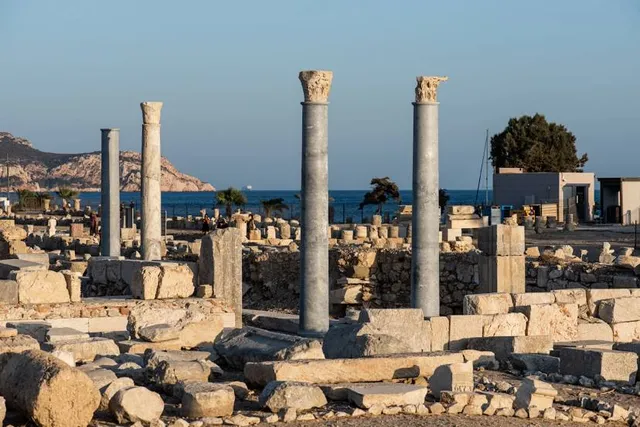
Knidos Ancient City
Yazı, Çevre Yolu, 48900 Datça/Muğla, Türkiye
4.6(4K)
Closed
Save
spot
spot
Ratings & Description
Info
Cultural
Outdoor
N/a
attractions: , restaurants: , local businesses:
 Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.
Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.Phone
+90 252 412 14 59
Website
kulturportali.gov.tr
Open hoursSee all hours
Mon9 AM - 7 PMClosed
Plan your stay

Pet-friendly Hotels in Datça
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Affordable Hotels in Datça
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

The Coolest Hotels You Haven't Heard Of (Yet)
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Trending Stays Worth the Hype in Datça
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.
Reviews
Live events

Your mosaic mirror
Tue, Feb 10 • 9:00 AM
853 00, Kos, Greece
View details