The major cities of the Indus Valley Civilisation, such as Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, date back to around 3300 BC, and represent some of the largest human habitations of the ancient world. The Indus Valley Civilisation extended from across northeast Afghanistan to Pakistan and northwest India,31] with an upward reach from east of Jhelum River to Ropar on the upper Sutlej. The coastal settlements extended from Sutkagan Dor at the Pakistan, Iran border to Kutch in modern Gujarat, India. There is an Indus site on the Amu Darya at Shortughai in northern Afghanistan, and the Indus site Alamgirpur at the Hindon River is located only 28 km (17 mi) from Delhi. To date, over 1,052 cities and settlements have been found, mainly in the general region of the Ghaggar-Hakra River and its tributaries. Among the settlements were the major urban centres of Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, as well as Lothal, Dholavira, Ganeriwala, and Rakhigarhi. Only 40 Indus Valley sites have been discovered on the Indus and its tributaries.[32] However, it is notable that majority of the Indus script seals and inscribed objects discovered were found at sites along the Indus river.[a34]
Most scholars believe that settlements of Gandhara grave culture of the early Indo-Aryans flourished in Gandhara from 1700 BC to 600 BC, when Mohenjo-daro and Harappa had already been abandoned.
The Rigveda describes several rivers, including one named "Sindhu". The Rigvedic "Sindhu" is thought to be the present-day Indus river. It is attested 176 times in its text, 94 times in the plural, and most often used in the generic sense of "river". In the Rigveda, notably in the later hymns, the meaning of the word is narrowed to refer to the Indus river in particular, e.g. in the list of rivers mentioned in the hymn of Nadistuti sukta. The Rigvedic hymns apply a feminine gender to all the rivers mentioned therein, except for the Brahmaputra.
The word "India" is derived from the Indus River. In ancient times, "India" initially referred to those regions immediately along the east bank of the Indus, where are Punjab and Sindh now but by 300 BC, Greek writers including Herodotus and Megasthenes were applying the term to the entire subcontinent that extends much farther eastward.[35
The lower basin of the Indus forms a natural boundary between the Iranian Plateau and the Indian subcontinent; this region embraces all or parts of the Pakistani provinces Balochistan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Punjab and Sindh and the countries Afghanistan and India. The first West Eurasian empire to annex the Indus Valley was the Persian Empire, during the reign of Darius the Great. During his reign, the Greek explorer Scylax of Caryanda was commissioned to explore the course of the Indus. It was crossed by the invading armies of Alexander, but after his Macedonians conquered the west bank—joining it to the Hellenic world, they elected to retreat along the southern course of the river, ending Alexander's Asian campaign. Alexander's admiral Nearchus set out from the Indus Delta to explore the Persian Gulf, until reaching the Tigris River. The Indus Valley was later dominated by the Mauryan and Kushan Empires, Indo-Greek Kingdoms, Indo-Scythians and Hepthalites. Over several centuries Muslim armies of Muhammad ibn al-Qasim, Mahmud of Ghazni, Muhammad of Ghor, Timur and Babur crossed the river to invade Sindh and Punjab, providing a gateway to the Indian...
Read more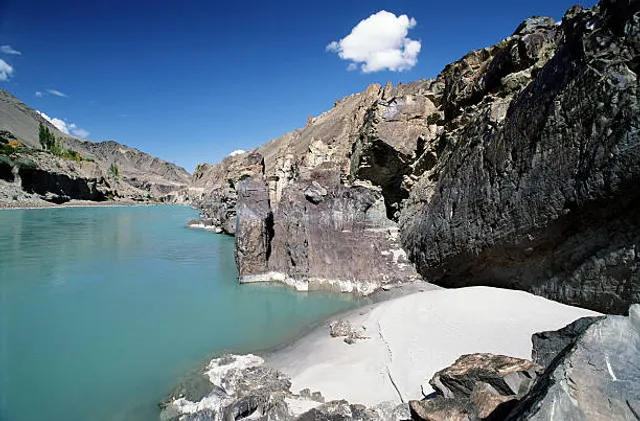
 Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.
Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.