Liangzhu Museum things to do, attractions, restaurants, events info and trip planning

Basic Info
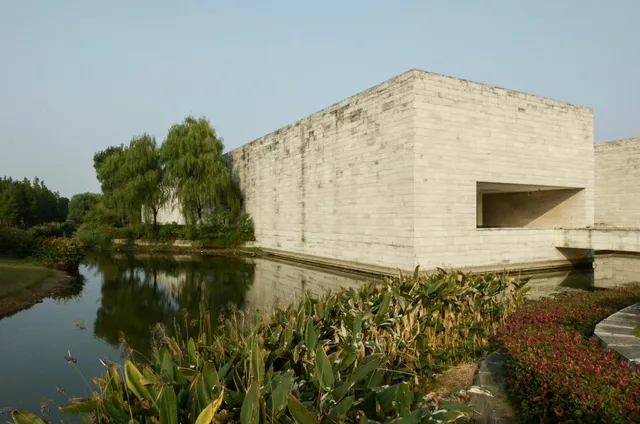
Liangzhu Museum
Yuhang District, Hangzhou, China, 311113
4.3(24)
Open 24 hours
Save
spot
spot
Ratings & Description
Info
The Liangzhu Museum is an archaeological museum dedicated to the Neolithic Liangzhu culture. It houses a collection of artefacts from the archaeological culture. It is located in Liangzhu, in the northwestern outskirts of Hangzhou, the capital of Zhejiang Province, China.
Cultural
Family friendly
Accessibility
attractions: , restaurants: , local businesses:
 Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.
Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.Plan your stay

Pet-friendly Hotels in Hangzhou City
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Affordable Hotels in Hangzhou City
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

The Coolest Hotels You Haven't Heard Of (Yet)
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Trending Stays Worth the Hype in Hangzhou City
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.