The Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park things to do, attractions, restaurants, events info and trip planning
Basic Info
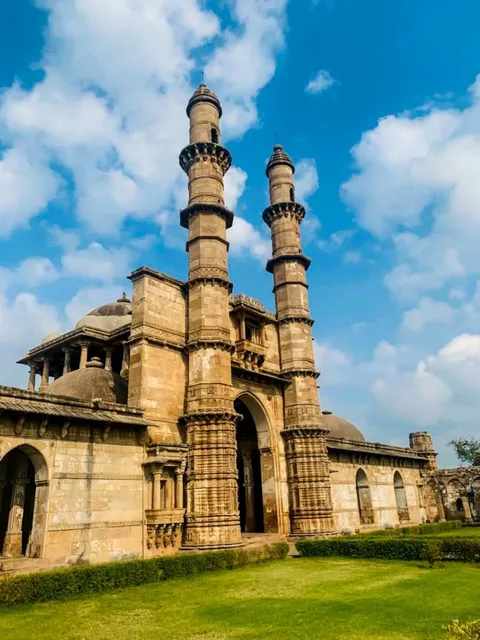
The Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park
Champaner, Gujarat 389360, India
4.4(2.7K)
Open 24 hours


tickets
Save
spot
spot
Ratings & Description
Info
Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is located in Panchmahal district in Gujarat, India. It is located around the historical city of Champaner, a city which was founded by Vanraj Chavda, the most prominent king of the Chavda Dynasty, in the eighth century.
Cultural
Outdoor
Family friendly
attractions: Jami Masjid, Champaner, Kevada Masjid مسجد, restaurants: Chapaner, Harsiddhi Nasta House, Shiv Shakti Hotel, Ravechi restaurant and cold drinks, SHIV PUNJABI CORNER, Vijay Laxmi Paubhaji, Jay Ranchhodray Bhojanalay, local businesses: Shaher ki Masjid, Pavagadh Shwetambar Jain Mandir
 Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.
Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.Phone
+91 1800 203 1111
Plan your stay

Pet-friendly Hotels in Champaner
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Affordable Hotels in Champaner
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

The Coolest Hotels You Haven't Heard Of (Yet)
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Trending Stays Worth the Hype in Champaner
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.
Reviews
Nearby attractions of The Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park
Jami Masjid, Champaner
Kevada Masjid مسجد

Jami Masjid, Champaner
4.4
(358)
Open until 6:00 PM
Click for details
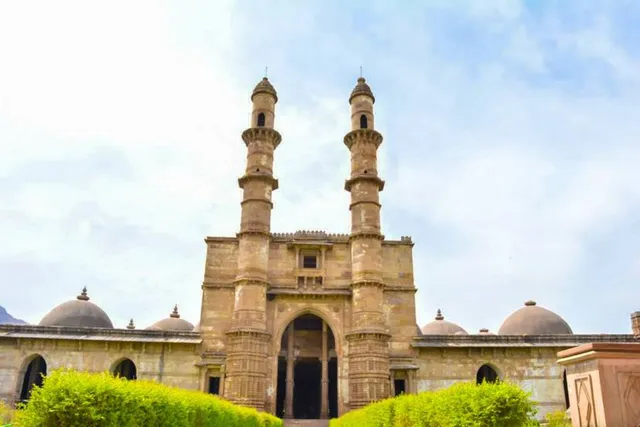

Kevada Masjid مسجد
4.4
(144)
Open until 6:00 PM
Click for details
Nearby restaurants of The Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park
Chapaner
Harsiddhi Nasta House
Shiv Shakti Hotel
Ravechi restaurant and cold drinks
SHIV PUNJABI CORNER
Vijay Laxmi Paubhaji
Jay Ranchhodray Bhojanalay

Chapaner
4.0
(5)
Click for details

Harsiddhi Nasta House
3.2
(4)
Click for details
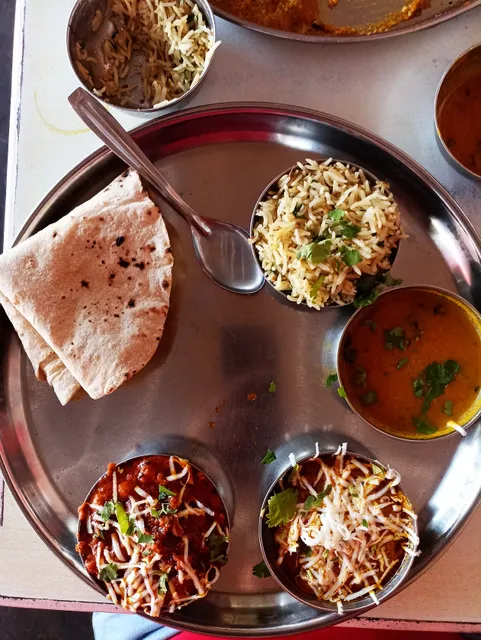

Shiv Shakti Hotel
4.1
(41)
Open until 4:00 PM
Click for details

Ravechi restaurant and cold drinks
4.4
(6)
Open until 11:30 PM
Click for details
Nearby local services of The Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park
Shaher ki Masjid
Pavagadh Shwetambar Jain Mandir
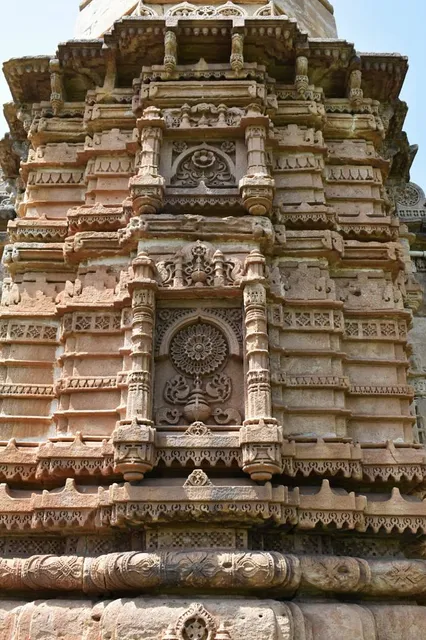

Shaher ki Masjid
4.3
(89)
Click for details

Pavagadh Shwetambar Jain Mandir
4.4
(341)
Click for details