Archaeological Museum Khajuraho things to do, attractions, restaurants, events info and trip planning

Basic Info
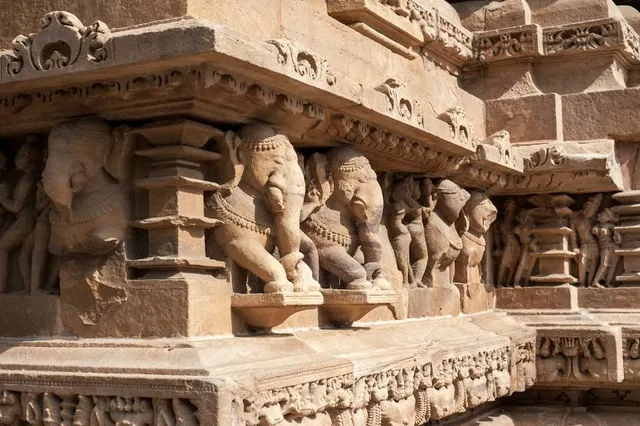
Archaeological Museum Khajuraho
VW59+VWJ, Rajnagar Rd, Sevagram, Khajuraho, Madhya Pradesh 471606, India
4.2(332)
Open until 12:00 AM
Save
spot
spot
Ratings & Description
Info
Cultural
Family friendly
Accessibility
attractions: Aadivart tribal museum khajuraho, Khajuraho Temple, Khajuraho Western Group of Temples, Chitragupta Temple, Kandariya Mahadeva Temple, Vishwanath Temple, Parvati Temple, Shree Matangeshwar Temple Khajuraho, Devi Jagadambi Temple, Varaha Temple, restaurants: Raja Cafe Restaurant , Khajuraho, Mosaic Cafe & Restro, Maharaja Cafe & Restaurant, Saffron cafe restaurant, Aqueen Chicken curry & Biryani, Zaheer Paratha & Lassi Corner, La Bella Italia Restaurant, Lala ji ki rasoi pure veg, MADRAS COFFEE HOUSE, le rose cafe, local businesses: Shivsagar Lake
 Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.
Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.Open hoursSee all hours
FriClosedOpen
Plan your stay

Pet-friendly Hotels in Khajuraho
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Affordable Hotels in Khajuraho
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

The Coolest Hotels You Haven't Heard Of (Yet)
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Trending Stays Worth the Hype in Khajuraho
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.
Reviews
Nearby attractions of Archaeological Museum Khajuraho
Aadivart tribal museum khajuraho
Khajuraho Temple
Khajuraho Western Group of Temples
Chitragupta Temple
Kandariya Mahadeva Temple
Vishwanath Temple
Parvati Temple
Shree Matangeshwar Temple Khajuraho
Devi Jagadambi Temple
Varaha Temple
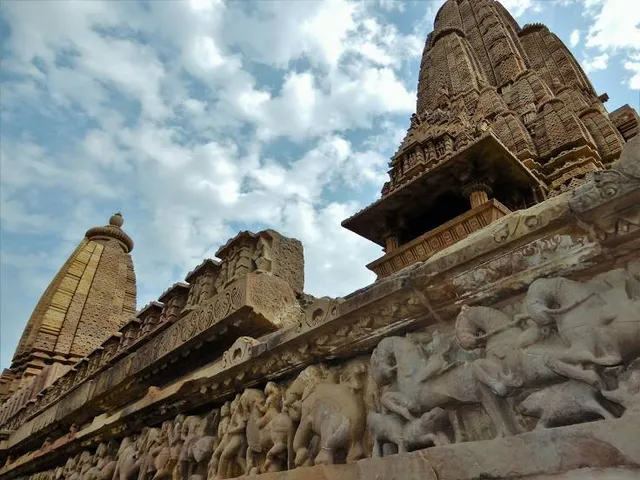

Aadivart tribal museum khajuraho
4.5
(419)
Open until 9:00 PM
Click for details
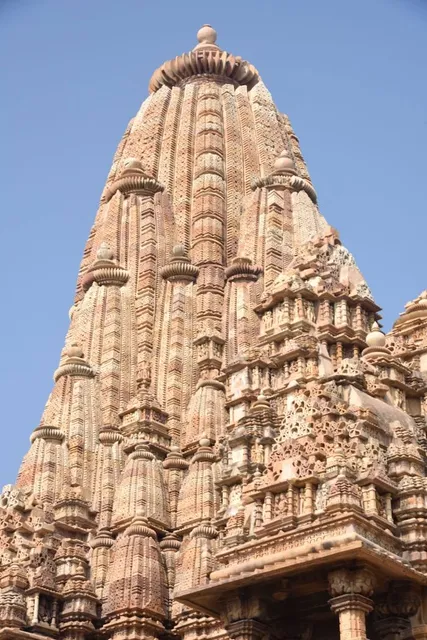

Khajuraho Temple
4.7
(4K)
Closed
Click for details
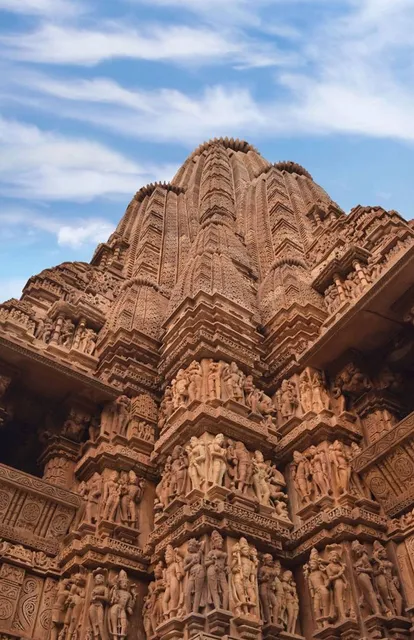

Khajuraho Western Group of Temples
4.7
(3.2K)
Closed
Click for details
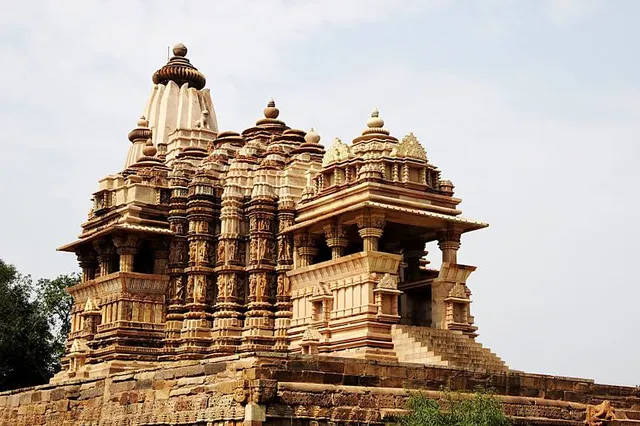

Chitragupta Temple
4.6
(129)
Closed
Click for details
Nearby restaurants of Archaeological Museum Khajuraho
Raja Cafe Restaurant , Khajuraho
Mosaic Cafe & Restro
Maharaja Cafe & Restaurant
Saffron cafe restaurant
Aqueen Chicken curry & Biryani
Zaheer Paratha & Lassi Corner
La Bella Italia Restaurant
Lala ji ki rasoi pure veg
MADRAS COFFEE HOUSE
le rose cafe

Raja Cafe Restaurant , Khajuraho
4.1
(793)
Open until 10:00 PM
Click for details
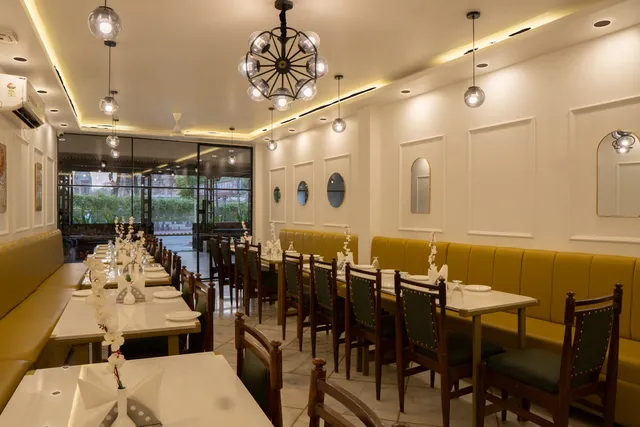

Mosaic Cafe & Restro
4.9
(86)
Open until 11:00 PM
Click for details

Maharaja Cafe & Restaurant
3.8
(103)
Open until 10:00 PM
Click for details

Saffron cafe restaurant
3.9
(53)
Open until 9:00 PM
Click for details
Nearby local services of Archaeological Museum Khajuraho
Shivsagar Lake

Shivsagar Lake
4.1
(29)
Click for details