Dubai Museum things to do, attractions, restaurants, events info and trip planning

Basic Info
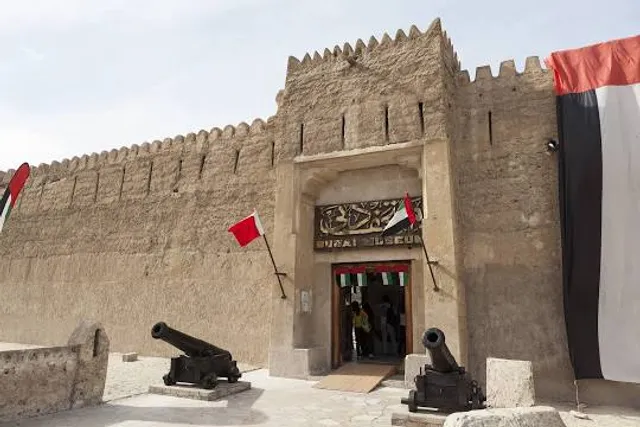
Dubai Museum
Al Fahidi Fort - Al Souq Al Kabeer - Al Fahidi - Dubai - United Arab Emirates
4.3(5.5K)
Open 24 hours
Save
spot
spot
Ratings & Description
Info
Cultural
Accessibility
attractions: Grand Bur Dubai Masjid, Al Fahidi Historical Neighbourhood, Bur Dubai Souk Market, Coffee Museum, Wall of Old Dubai, Deira Creek 🛥️, Sheikh Mohammed Centre for Cultural Understanding, XVA Gallery, Coins Museum Bur Dubai, The Majlis Gallery, restaurants: Mumtaz Mahal Indian Speciality Restaurant | Best Restaurant in Bur Dubai, Arabian Tea House Restaurant & Cafe - Al Fahidi, Dubai, Veganesha, Mumbai Masti Juice Center, Al Khayma Heritage Restaurant | مطعم الخيمة التراثي, Chinese Dynasty Restaurant | Best Chinese Food in Dubai, NEW KABAB AL MADINA Restaurant 2OURIST CAFE & ARABIC FOOD CORNER, Creek City Restaurant, Tasty Bite Restaurant, Taj Mahal Palace Restaurant, local businesses: Meena Bazar Burdubai, Textile wholesale market Bur Dubai, AYAL PERFUMES - BUR DUBAI, Dubai Spice Souk, Abra Deira dubai, Kanz Jewels Gold Souk, Chuk Palu Rugs ( Fashion for the Floor ), Old Souk, Central Mall, Dubai Creek
 Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.
Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.Phone
+971 800 33222
Website
dubaiculture.gov.ae
Plan your stay

Pet-friendly Hotels in Dubai
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Affordable Hotels in Dubai
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

The Coolest Hotels You Haven't Heard Of (Yet)
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Trending Stays Worth the Hype in Dubai
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.
Reviews
Live events

Experience Luxury desert safari in Dubai
Sun, Feb 22 • 1:15 PM
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
View details

Arte Museum Dubai: An Immersive Media Art Exhibition
Sun, Feb 22 • 10:00 AM
Dubai Mall - opposite Galeries Lafayette - Level 2 Financial Center street - Dubai, UAE
View details
Nearby attractions of Dubai Museum
Grand Bur Dubai Masjid
Al Fahidi Historical Neighbourhood
Bur Dubai Souk Market
Coffee Museum
Wall of Old Dubai
Deira Creek 🛥️
Sheikh Mohammed Centre for Cultural Understanding
XVA Gallery
Coins Museum Bur Dubai
The Majlis Gallery

Grand Bur Dubai Masjid
4.7
(906)
Open until 12:00 AM
Click for details

Al Fahidi Historical Neighbourhood
4.6
(6.3K)
Open 24 hours
Click for details
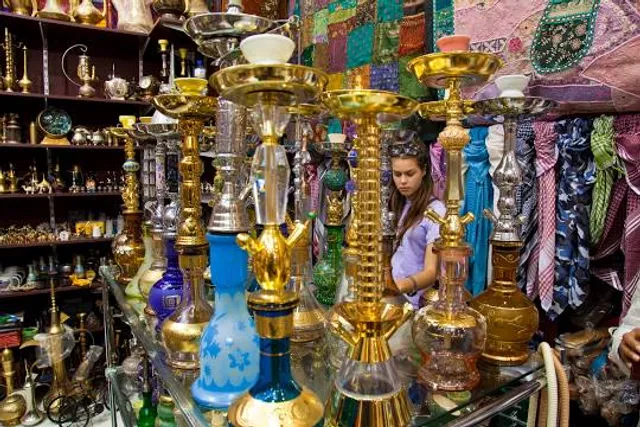

Bur Dubai Souk Market
4.4
(5.3K)
Closed
Click for details
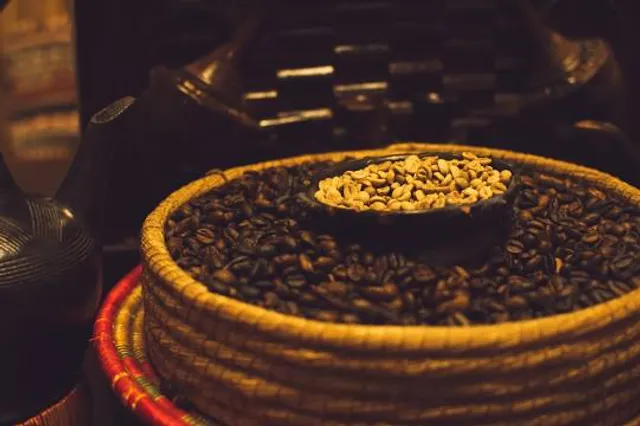

Coffee Museum
4.4
(685)
Closed
Click for details
Nearby restaurants of Dubai Museum
Mumtaz Mahal Indian Speciality Restaurant | Best Restaurant in Bur Dubai
Arabian Tea House Restaurant & Cafe - Al Fahidi, Dubai
Veganesha
Mumbai Masti Juice Center
Al Khayma Heritage Restaurant | مطعم الخيمة التراثي
Chinese Dynasty Restaurant | Best Chinese Food in Dubai
NEW KABAB AL MADINA Restaurant 2OURIST CAFE & ARABIC FOOD CORNER
Creek City Restaurant
Tasty Bite Restaurant
Taj Mahal Palace Restaurant

Mumtaz Mahal Indian Speciality Restaurant | Best Restaurant in Bur Dubai
4.6
(767)
$$
Closed
Click for details
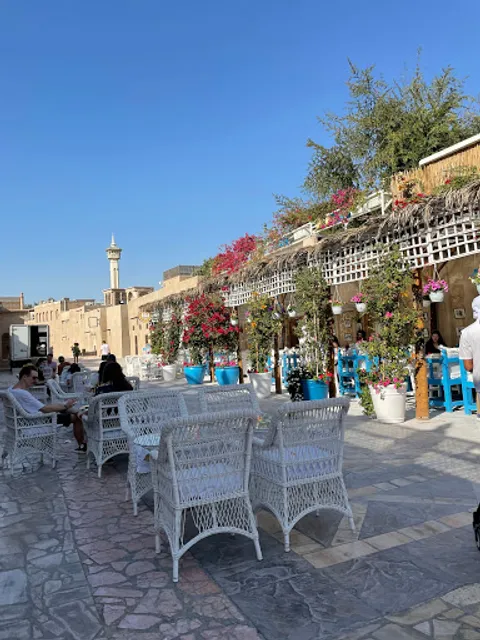

Arabian Tea House Restaurant & Cafe - Al Fahidi, Dubai
4.8
(7.7K)
Closed
Click for details
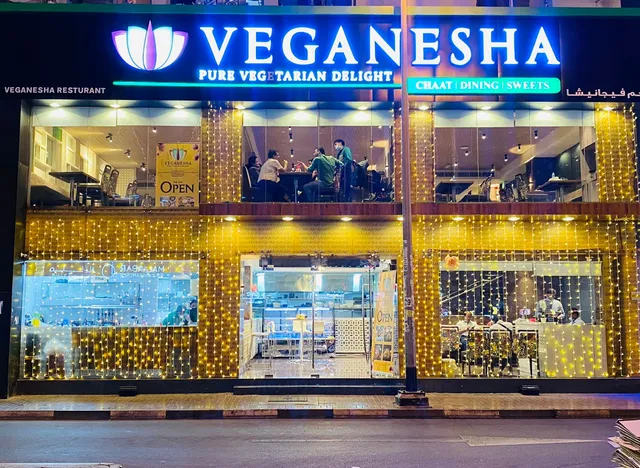

Veganesha
4.8
(1.4K)
Closed
Click for details

Mumbai Masti Juice Center
4.2
(865)
Closed
Click for details
Nearby local services of Dubai Museum
Meena Bazar Burdubai
Textile wholesale market Bur Dubai
AYAL PERFUMES - BUR DUBAI
Dubai Spice Souk
Abra Deira dubai
Kanz Jewels Gold Souk
Chuk Palu Rugs ( Fashion for the Floor )
Old Souk
Central Mall
Dubai Creek

Meena Bazar Burdubai
4.4
(2.2K)
Click for details

Textile wholesale market Bur Dubai
4.1
(629)
Click for details

AYAL PERFUMES - BUR DUBAI
4.8
(47)
Click for details

Dubai Spice Souk
4.3
(2.7K)
Click for details