French Huguenot Church things to do, attractions, restaurants, events info and trip planning

Basic Info
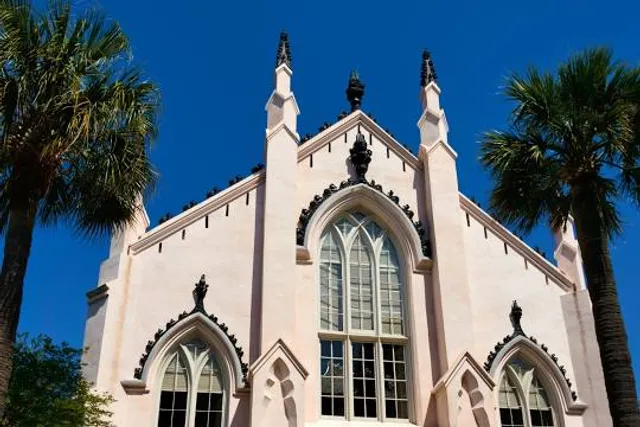
French Huguenot Church
Location of Church: 136 Church Street Charleston, SC 29401 Mailing Address: P. O. Drawer 917, Church St, Charleston, SC 29402
4.7(94)
Open 24 hours
Save
spot
spot
Ratings & Description
Info
The Huguenot Church, also called the French Huguenot Church or the French Protestant Church, is a Gothic Revival church located at 136 Church Street in Charleston, South Carolina.
Cultural
Accessibility
attractions: Old Slave Mart Museum, Dock Street Theatre, St. Philip's Church, French Quarter District, Queen Street Playhouse: Home of the Footlight Players, Washington Square, Joe Riley Waterfront Park, Old South Carriage Company, Robert Lange Studios Art Gallery, Old Exchange and Provost Dungeon, restaurants: Blind Tiger Pub, Magnolias, Toast! All Day Meeting Street, Pearlz Oyster Bar, Harken Cafe, Tommy Condon's Irish Pub & Restaurant, Poogan's Porch, The Rooftop at the Vendue, Ru Ru's Tacos & Tequila, Iron Rose, local businesses: Charleston Walking Tours by Charleston Footprints, Charleston Tour Company, 82 Queen St, Charleston History Walk, Bringardner Injury Law Firm, Ty Robinson Personal Injury & Car Accident Law Firm Charleston, Magnolia Med Spa, JK Designs Jewelry, Theos Law Firm, Charleston Pirate Tours
 Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.
Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.Phone
(843) 722-4385
Website
huguenot-church.org
Plan your stay

Pet-friendly Hotels in Charleston
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Affordable Hotels in Charleston
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

The Coolest Hotels You Haven't Heard Of (Yet)
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Trending Stays Worth the Hype in Charleston
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.
Reviews
Live events

Candlelight: Tribute to Coldplay
Fri, Feb 27 • 6:30 PM
4 Archdale St, Charleston, SC 29401, 29401
View details

1.5-Hour Charleston Harbor Cruise with Live Narration
Fri, Feb 27 • 11:00 AM
Mount Pleasant, 29403
View details

The Day Club Party
Sat, Feb 28 • 2:00 PM
1734 Signal Point Road Charleston, SC 29412
View details
Nearby attractions of French Huguenot Church
Old Slave Mart Museum
Dock Street Theatre
St. Philip's Church
French Quarter District
Queen Street Playhouse: Home of the Footlight Players
Washington Square
Joe Riley Waterfront Park
Old South Carriage Company
Robert Lange Studios Art Gallery
Old Exchange and Provost Dungeon
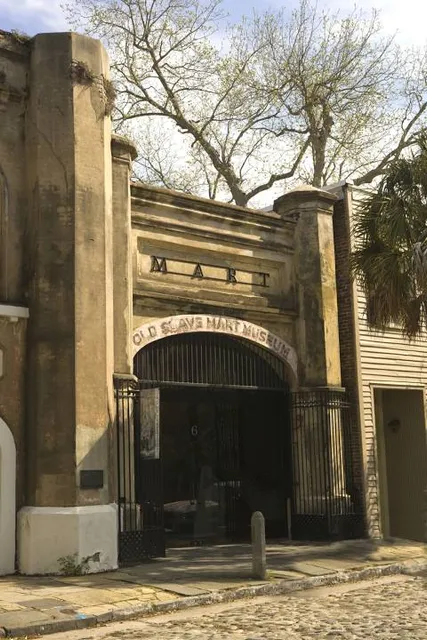

Old Slave Mart Museum
4.4
(1.2K)
Open until 5:00 PM
Click for details
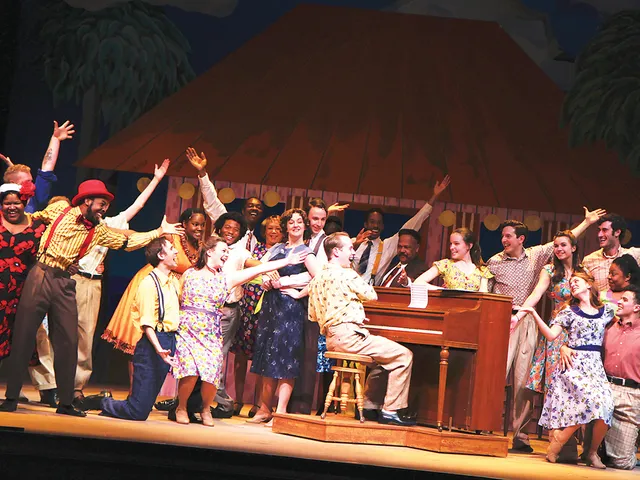

Dock Street Theatre
4.8
(464)
Open 24 hours
Click for details
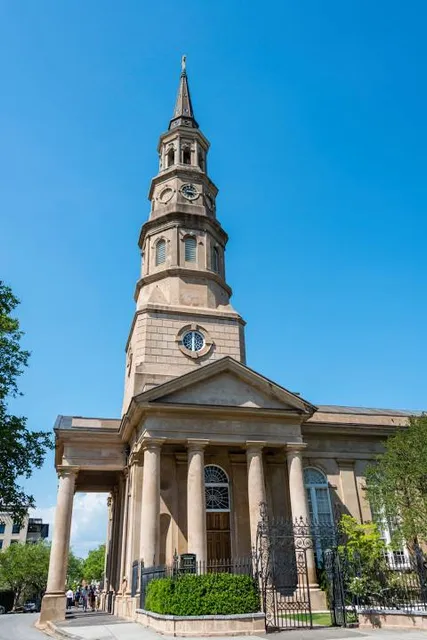

St. Philip's Church
4.8
(179)
Open until 12:00 AM
Click for details
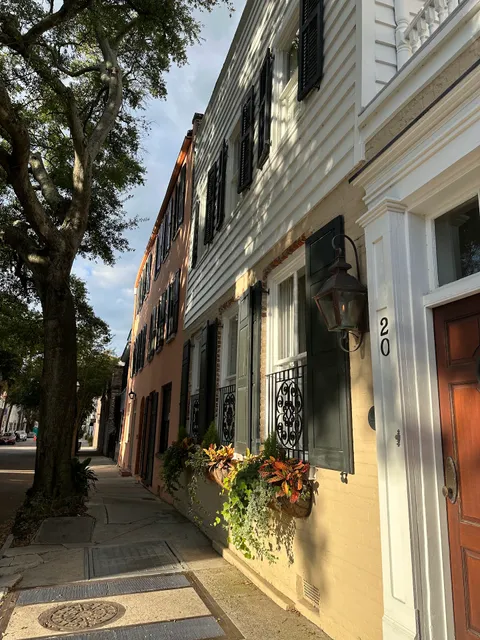

French Quarter District
4.4
(182)
Open 24 hours
Click for details
Nearby restaurants of French Huguenot Church
Blind Tiger Pub
Magnolias
Toast! All Day Meeting Street
Pearlz Oyster Bar
Harken Cafe
Tommy Condon's Irish Pub & Restaurant
Poogan's Porch
The Rooftop at the Vendue
Ru Ru's Tacos & Tequila
Iron Rose

Blind Tiger Pub
4.4
(1.4K)
$$
Open until 1:30 AM
Click for details
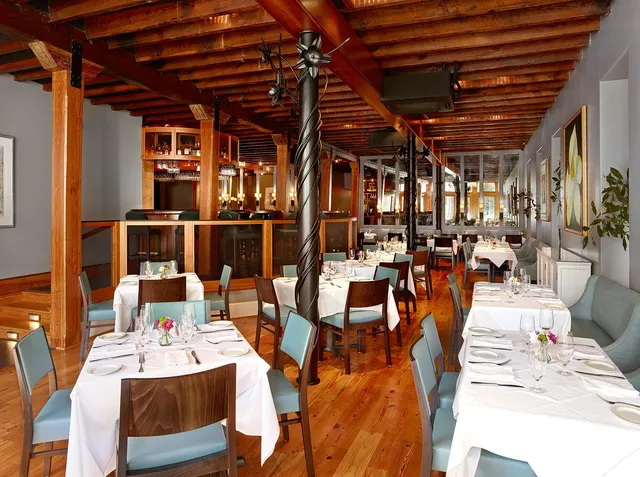

Magnolias
4.7
(2.2K)
$$$
Open until 3:30 PM
Click for details
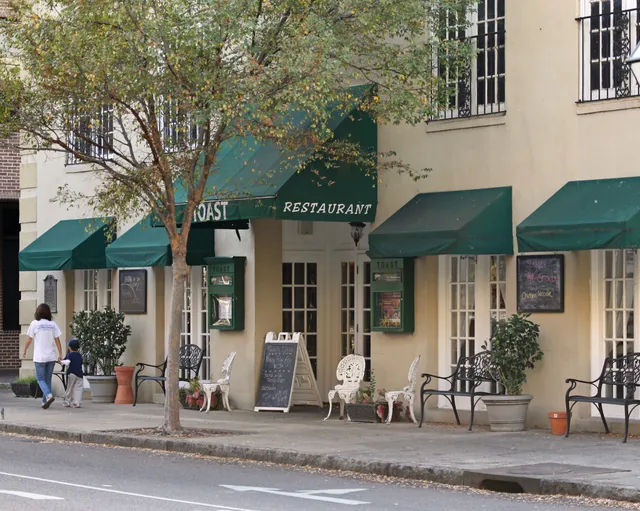

Toast! All Day Meeting Street
4.4
(2.5K)
$
Open until 3:00 PM
Click for details

Pearlz Oyster Bar
4.6
(986)
$$
Open until 9:00 PM
Click for details
Nearby local services of French Huguenot Church
Charleston Walking Tours by Charleston Footprints
Charleston Tour Company
82 Queen St
Charleston History Walk
Bringardner Injury Law Firm
Ty Robinson Personal Injury & Car Accident Law Firm Charleston
Magnolia Med Spa
JK Designs Jewelry
Theos Law Firm
Charleston Pirate Tours
Charleston Walking Tours by Charleston Footprints
4.9
(194)
Click for details

Charleston Tour Company
5.0
(436)
Click for details
82 Queen St
4.5
(1.5K)
Click for details

Charleston History Walk
5.0
(109)
Click for details
The hit list

Plan your trip with Wanderboat
Welcome to Wanderboat AI, your AI search for local Eats and Fun, designed to help you explore your city and the world with ease.
Powered by Wanderboat AI trip planner.