Basilica di San Francesco things to do, attractions, restaurants, events info and trip planning

Basic Info
Basilica di San Francesco
Piazza Malpighi, 9, 40123 Bologna BO, Italy
4.6(23)
Closed
Save
spot
spot
Ratings & Description
Info
Cultural
Historical significance
attractions: Mercato delle Erbe, Palazzo Pallavicini, Portico delle Parole, Museo Illusione tra arte e scienza a Palazzo Belloni, Ex Chiesa di San Mattia, Piazza Maggiore, Palazzo Albergati, Neptune's Fountain, Cattedrale Metropolitana di San Pietro, Biblioteca Salaborsa, restaurants: Trattoria Fantoni, Altotasso, Osteria Bartolini, Macondo - Cocktail Bar, Caffè De Marchi, Maritozzi e Gelato di Barbara e Renato, Zapap Pratello, 'O Fiore Mio Pizze di Strada, Favilla, Doppio Malto Bologna Malpighi, local businesses: Flying Tiger Copenhagen, Felcaro - Arredamento, mobili e sedute, MINISO, Palazzo Belloni, Mercatino di Beneficenza di San Francesco, Filipino Store, Pop Up Cinema Jolly 4K, Mercato dei Fiori di San Francesco, PizzAltero, Goblin
 Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.
Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.Phone
+39 051 221762
Website
sanfrancescobologna.org
Open hoursSee all hours
Fri7 AM - 12 PM, 3:30 - 7 PMClosed
Plan your stay

Pet-friendly Hotels in Bologna
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Affordable Hotels in Bologna
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

The Coolest Hotels You Haven't Heard Of (Yet)
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Trending Stays Worth the Hype in Bologna
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.
Reviews
Live events
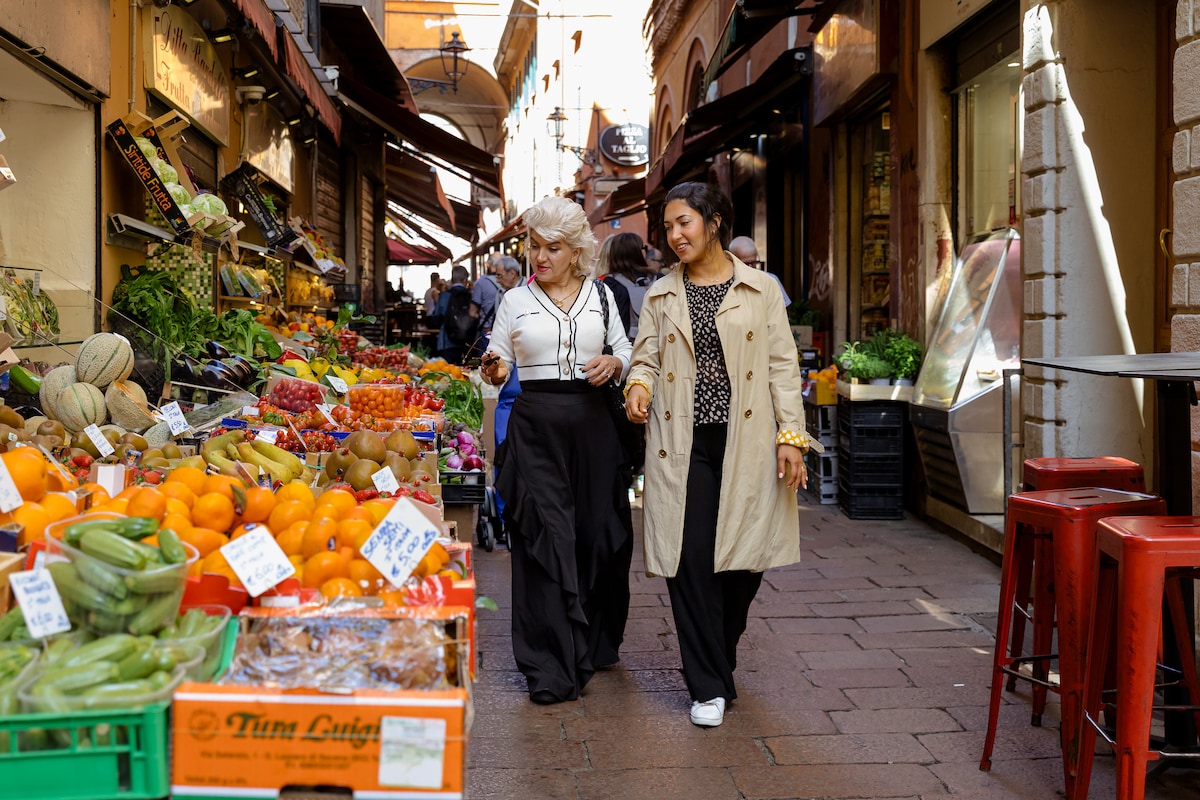

Exploring the Secrets of Bologna
Fri, Feb 6 • 2:00 PM
40124, Bologna, Emilia-Romagna, Italy
View details
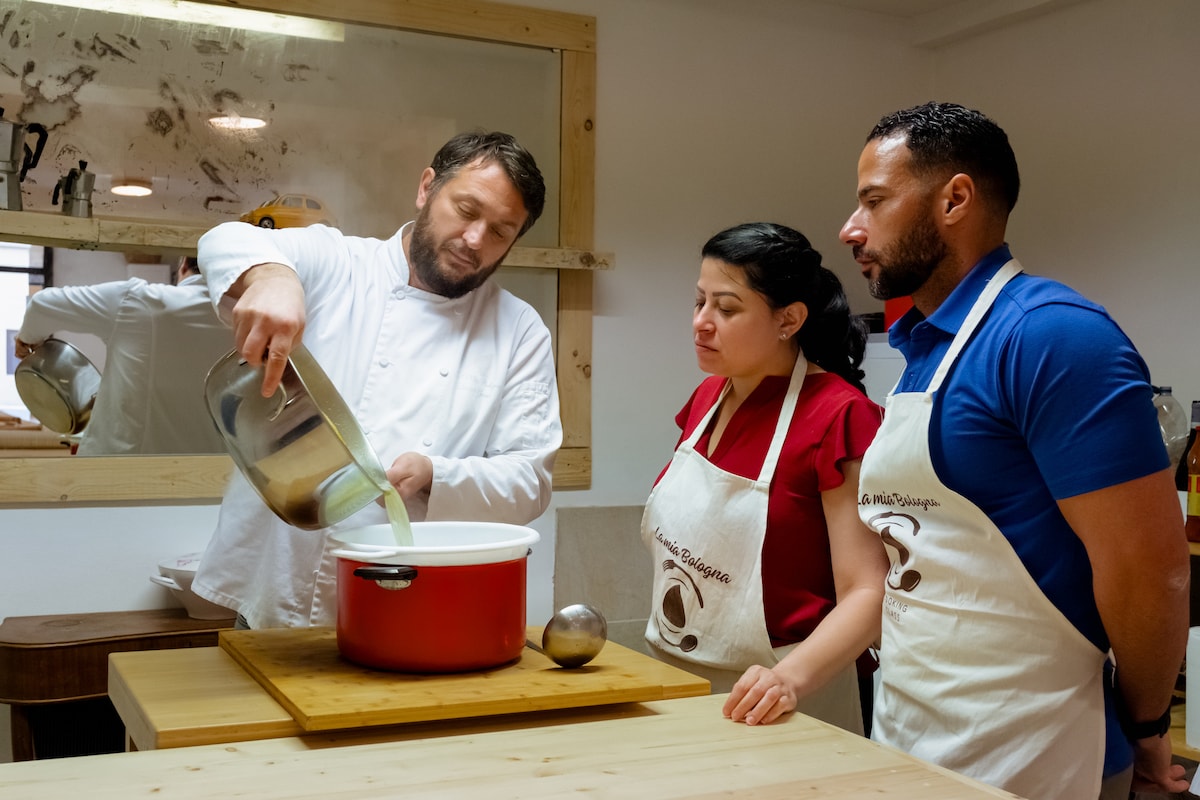

Prepare traditional dishes and local wine
Fri, Feb 6 • 10:00 AM
40120, Bologna, Emilia-Romagna, Italy
View details
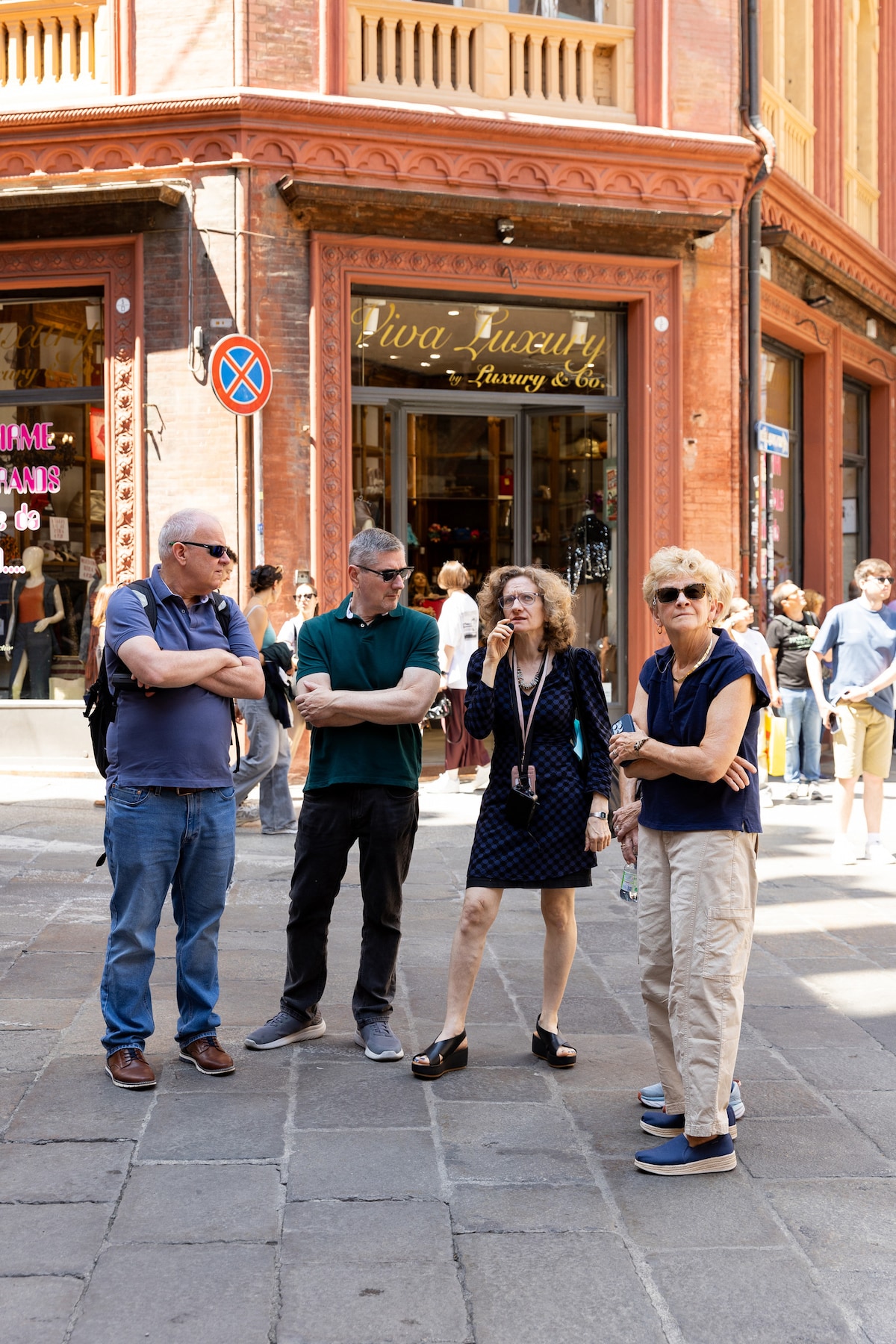

Take a journey through classical Bologna
Fri, Feb 6 • 10:30 AM
40131, Bologna, Emilia-Romagna, Italy
View details
Nearby attractions of Basilica di San Francesco
Mercato delle Erbe
Palazzo Pallavicini
Portico delle Parole
Museo Illusione tra arte e scienza a Palazzo Belloni
Ex Chiesa di San Mattia
Piazza Maggiore
Palazzo Albergati
Neptune's Fountain
Cattedrale Metropolitana di San Pietro
Biblioteca Salaborsa
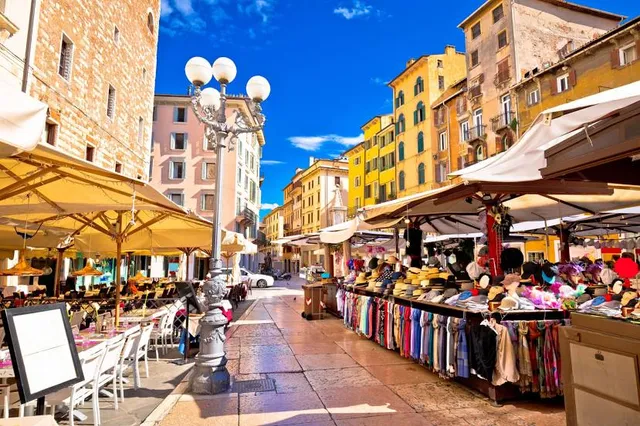

Mercato delle Erbe
4.3
(5.9K)
Closed
Click for details

Palazzo Pallavicini
4.5
(1.5K)
Closed
Click for details

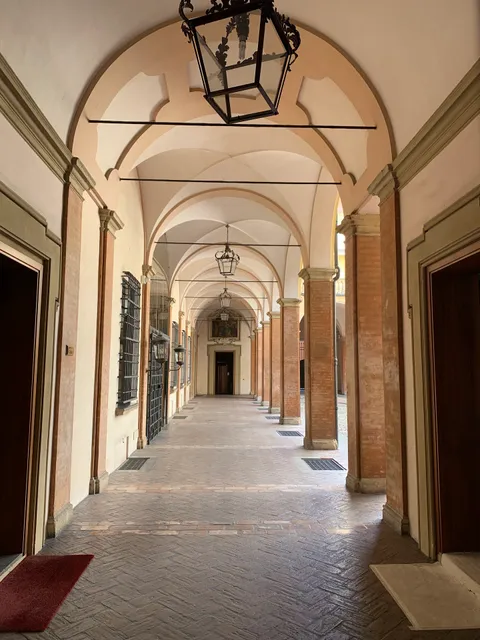
Portico delle Parole
5.0
(96)
Closed
Click for details

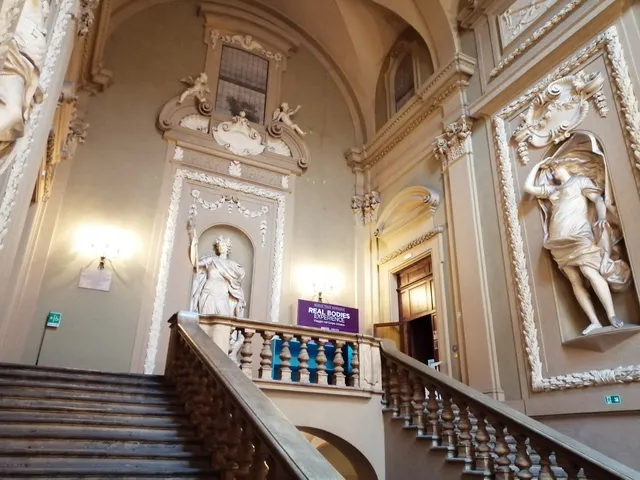
Museo Illusione tra arte e scienza a Palazzo Belloni
4.2
(483)
Closed
Click for details
Nearby restaurants of Basilica di San Francesco
Trattoria Fantoni
Altotasso
Osteria Bartolini
Macondo - Cocktail Bar
Caffè De Marchi
Maritozzi e Gelato di Barbara e Renato
Zapap Pratello
'O Fiore Mio Pizze di Strada
Favilla
Doppio Malto Bologna Malpighi
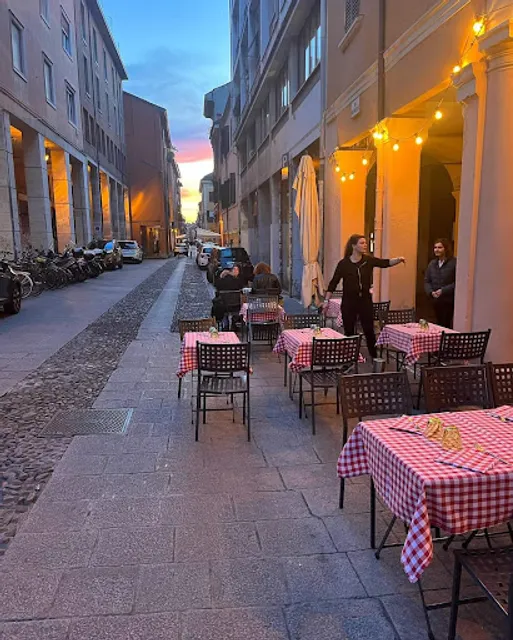

Trattoria Fantoni
4.3
(1.0K)
Closed
Click for details

Altotasso
4.1
(610)
Open until 4:00 AM
Click for details

Osteria Bartolini
4.3
(1.7K)
Closed
Click for details

Macondo - Cocktail Bar
4.3
(530)
Closed
Click for details
Nearby local services of Basilica di San Francesco
Flying Tiger Copenhagen
Felcaro - Arredamento, mobili e sedute
MINISO
Palazzo Belloni
Mercatino di Beneficenza di San Francesco
Filipino Store
Pop Up Cinema Jolly 4K
Mercato dei Fiori di San Francesco
PizzAltero
Goblin

Flying Tiger Copenhagen
4.2
(1.5K)
Click for details

Felcaro - Arredamento, mobili e sedute
4.6
(43)
Click for details

MINISO
4.3
(186)
Click for details

Palazzo Belloni
4.1
(332)
Click for details