Bou Inania Madrasa things to do, attractions, restaurants, events info and trip planning

Basic Info
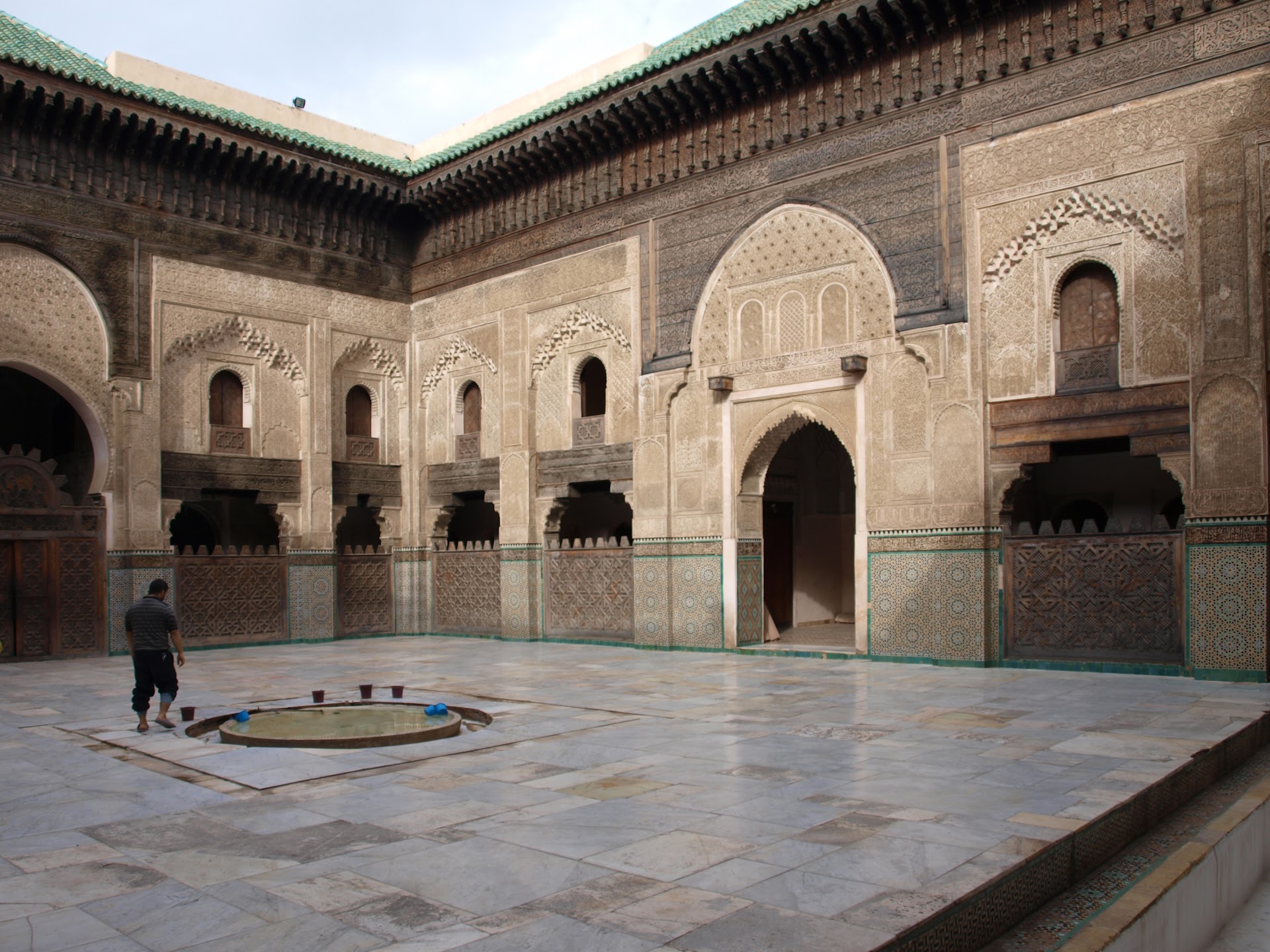
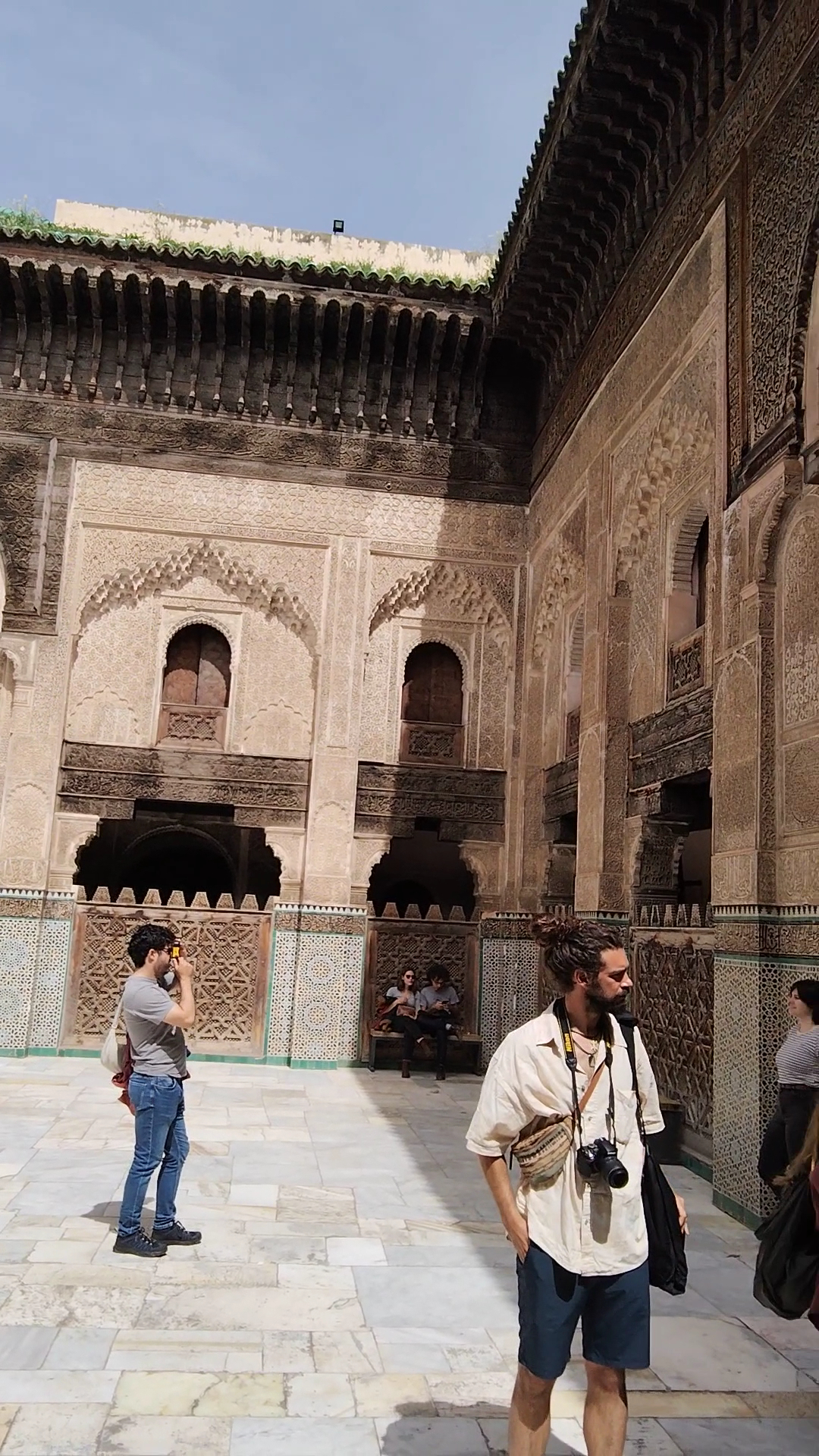
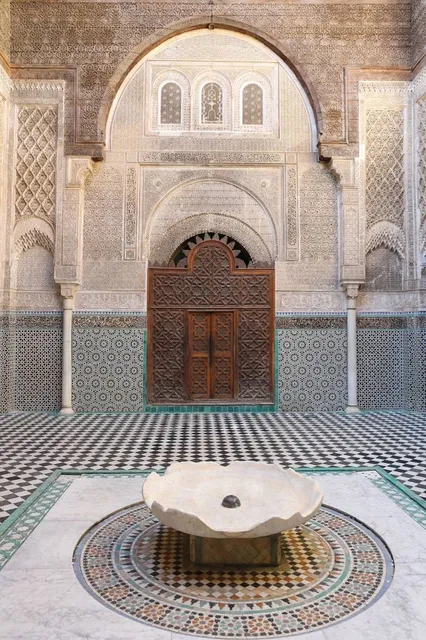
Bou Inania Madrasa
3268+WV7, Rue Talaa Sghira, Fès, Morocco
4.4(299)
Closed
Save
spot
spot
Ratings & Description
Info
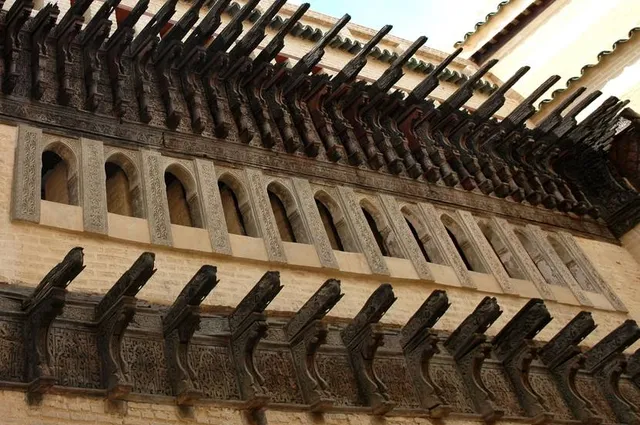
The Madrasa Bou Inania is a madrasa in Fes, Morocco, built in 1350–55 CE by Abu Inan Faris. It is the only madrasa in Morocco which also functioned as a congregational mosque. It is widely acknowledged as a high point of Marinid architecture and of historic Moroccan architecture generally.
Cultural
Scenic
Accessibility
attractions: Bab Boujloud, Fez Medina Pottery, Dar al-Magana (Water Clock), Bab Boujeloud, Bab Boujloud, Dar Batha Museum of Islamic Arts, Palais Mnebhi, Bab Mahrouk, ساحة أبي الجنود - Place Boujloud, Borj Nord Museum, restaurants: Cafe Clock, Mom's touch, Restaurant Bab Sahra Fes, Chez Rachid, Barbecue Alarbi Fes, Culture Box, Veggie pause, Restaurant boujloud, rujia 如家餐厅, Fez & Friends, local businesses: Hammam Mernissi & Spa, Rainbow Street Art, 3279+G4C, Blue Gate, 14 Rue de la poste, Coin Berbere, Sahara Desert Crew Tours, Médina de Fès, Sahara Desert Trips & Morocco Travels, Bab el-Hadid
 Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.
Learn more insights from Wanderboat AI.Open hoursSee all hours
Sat9 AM - 5 PMClosed
Plan your stay

Pet-friendly Hotels in Fez
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Affordable Hotels in Fez
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

The Coolest Hotels You Haven't Heard Of (Yet)
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.

Trending Stays Worth the Hype in Fez
Find a cozy hotel nearby and make it a full experience.
Reviews
Live events

Uncover Fez’s hidden secrets
Sat, Feb 21 • 2:30 PM
Fes, 30110, Morocco
View details

Moroccan vegetarian & vegan cooking & souk visit
Sun, Feb 22 • 3:30 PM
Fes, 30100, Morocco
View details
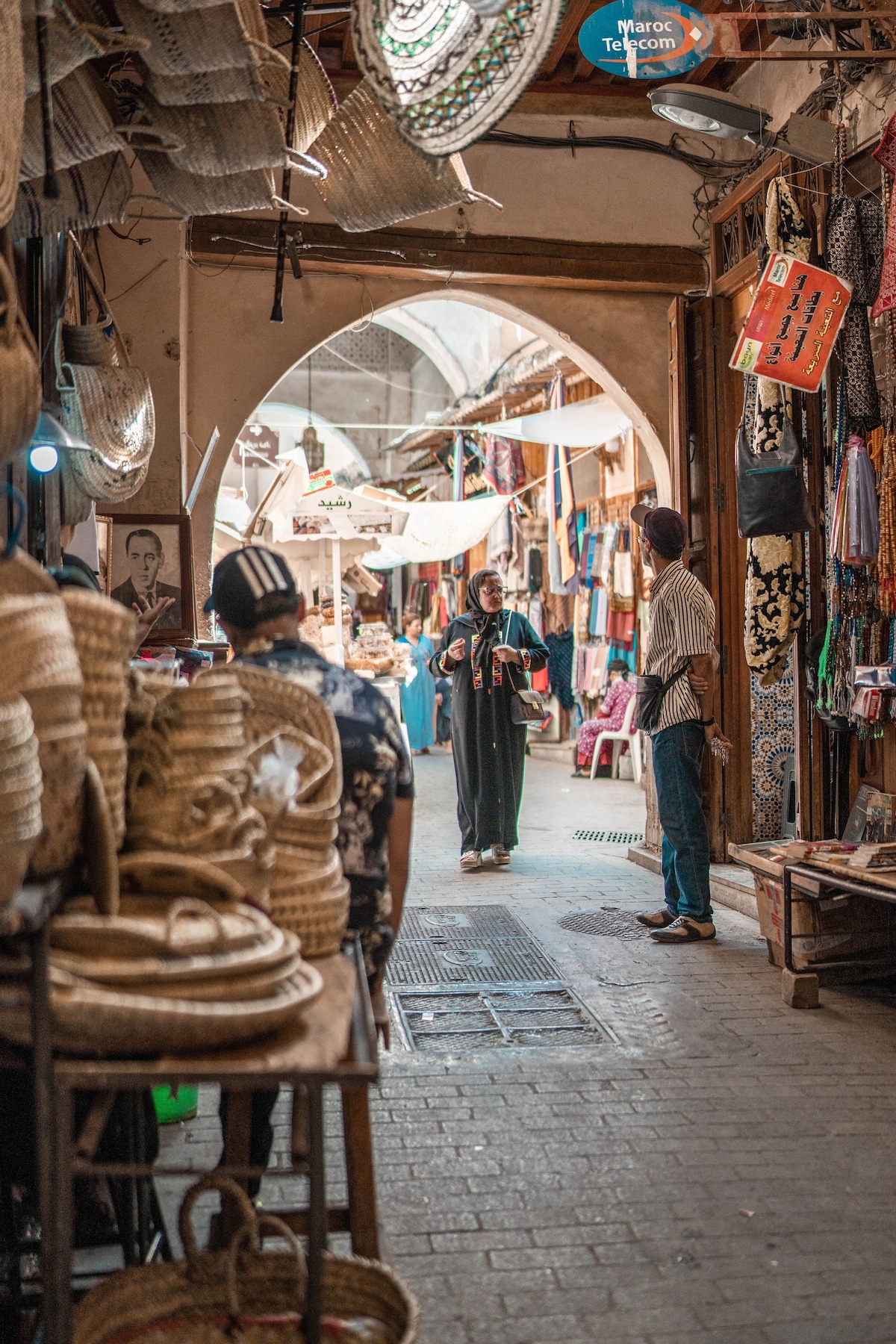

Beyond the maps and monuments the authentic Fez
Sat, Feb 21 • 10:00 AM
Fes, 00000, Morocco
View details
Nearby attractions of Bou Inania Madrasa
Bab Boujloud
Fez Medina Pottery
Dar al-Magana (Water Clock)
Bab Boujeloud
Bab Boujloud
Dar Batha Museum of Islamic Arts
Palais Mnebhi
Bab Mahrouk
ساحة أبي الجنود - Place Boujloud
Borj Nord Museum
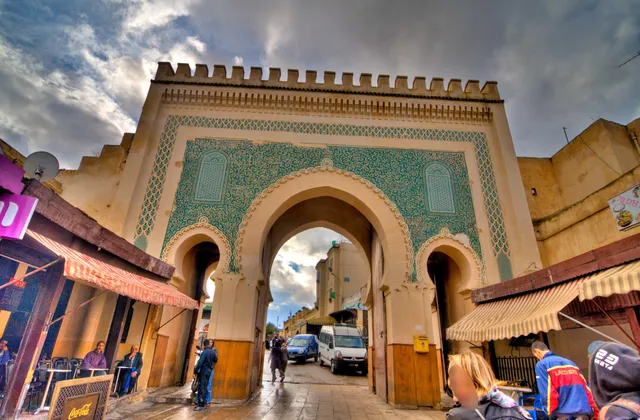

Bab Boujloud
4.4
(5.3K)
Closed
Click for details
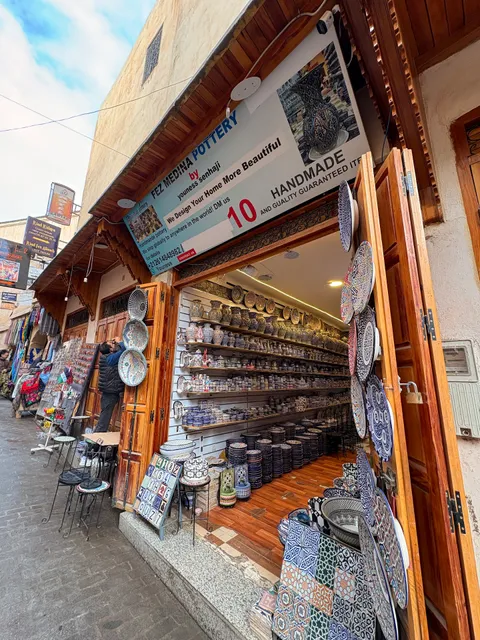

Fez Medina Pottery
5.0
(141)
Closed
Click for details

Dar al-Magana (Water Clock)
4.1
(54)
Open until 12:00 AM
Click for details
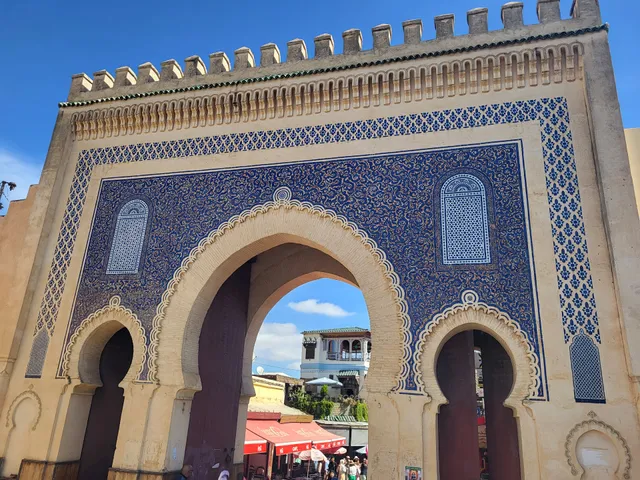

Bab Boujeloud
4.5
(169)
Open 24 hours
Click for details
Nearby restaurants of Bou Inania Madrasa
Cafe Clock
Mom's touch
Restaurant Bab Sahra Fes
Chez Rachid
Barbecue Alarbi Fes
Culture Box
Veggie pause
Restaurant boujloud
rujia 如家餐厅
Fez & Friends
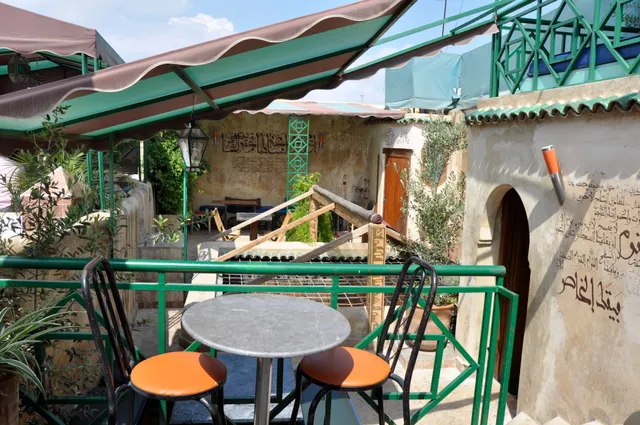

Cafe Clock
4.4
(1.9K)
Closed
Click for details
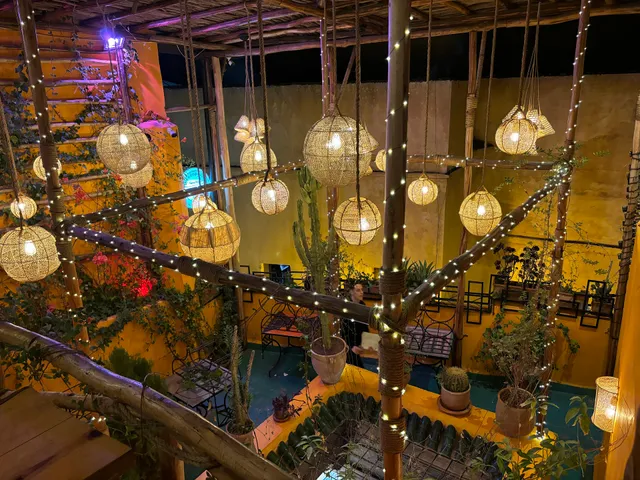

Mom's touch
4.6
(491)
Closed
Click for details
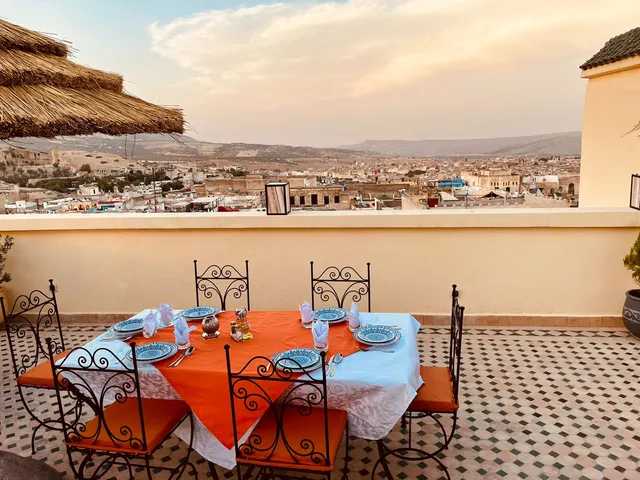

Restaurant Bab Sahra Fes
4.5
(306)
Click for details

Chez Rachid
4.5
(609)
Open until 12:00 AM
Click for details
Nearby local services of Bou Inania Madrasa
Hammam Mernissi & Spa
Rainbow Street Art
3279+G4C
Blue Gate
14 Rue de la poste
Coin Berbere
Sahara Desert Crew Tours
Médina de Fès
Sahara Desert Trips & Morocco Travels
Bab el-Hadid

Hammam Mernissi & Spa
4.4
(572)
Click for details

Rainbow Street Art
4.2
(33)
Click for details

3279+G4C
4.8
(238)
Click for details
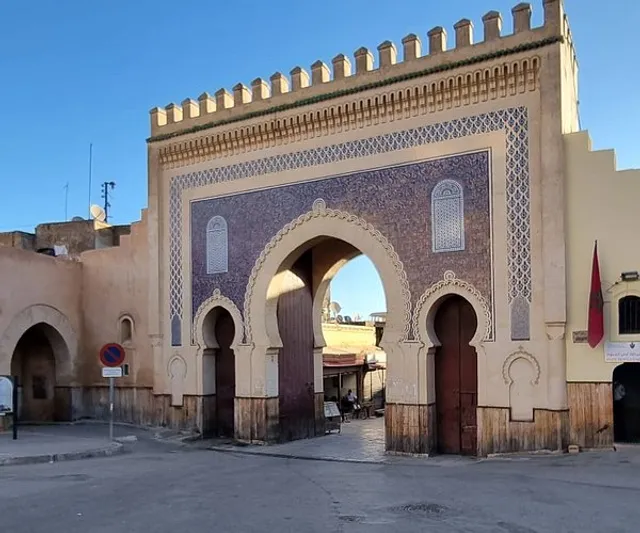

Blue Gate
4.5
(34)
Click for details